 Problems
Problems
Exposure to excessive noise pollution can cause disturbances to the psycho-physical health of the individual. Law no. 447/1995 art. 2 provides a correct and understandable definition of noise pollution: “the introduction of noise in the living environment or in the external environment such as to cause annoyance or disturbance to rest and human activities, danger to human health, deterioration of ecosystems, material assets, monuments, the living environment or the external environment or those that interfere with the normal functions of the environments themselves “. In the case of acoustic disturbances related to residence in a home, we distinguish those that are the noises coming from outside the building and more properly related to noise pollution (traffic from cars, trains, airplanes; commercial activities, restaurants, bars, etc.), from the noises generated inside the house such as: appliances, trampling, air conditioners and fan coils, hydraulic systems, lifts, all excessive behavior of neighbors (screams, shouts, music and loud sounds).

The safeguarding of our well-being within residential, work or leisure environments, or within public and receptive environments, is protected by a regulatory framework in Italy that is applied through the DPCM (Decree of the President of the Council of Ministers) 5/12/1997 on the “Passive acoustic requirements of buildings”. Through this legal device, in the construction or renovation of any building in Italy, a series of requirements must be respected, which limit the exposure of tenants to noise. In the case of “discontinuous systems” (this is how plumbing and heating systems are defined within the DPCM5 / 12/1997), the maximum limit of 35 decibels measured in the disturbed room must never be exceeded, whatever the intended use of the building is.
Reducing human exposure to noise is a fundamental element for the quality of living and a hygienic-sanitary requirement of the building which, in light of the acoustic standards, is no longer a subjective issue linked to the different sensitivities and perception of the individual, but a tangible and decisive value for living well-being. Considering today – in modern constructions – adequate acoustic insulation of the building envelope (obtained in combination with the thermal insulation imposed by Legislative Decree 311/06), basically when recording the sources of sound energy within a home, there are low levels of background noise. This accentuates our sensitivity and – especially in the quietest hours – the perception of noises inside the home becomes more significant and, in some respects, less tolerable. This leads to a greater susceptibility to disturbance with the consequent degradation of the level of comfort. Among the elements that most cause these disturbances are the drainage systems: pipes, sanitary appliances, toilet flush cisterns, siphons.
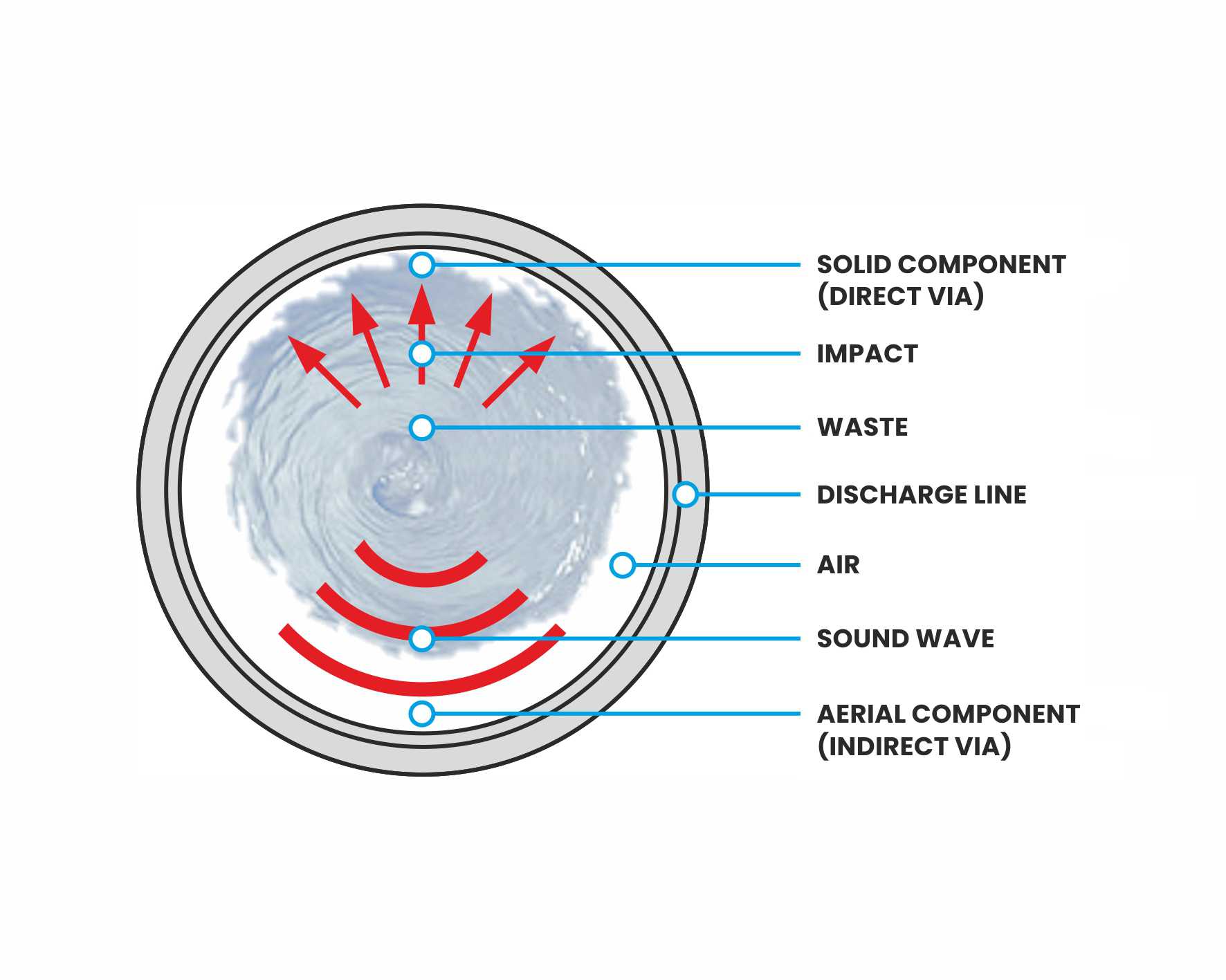
Knowing the principles of acoustic physics and the behavior of materials in relation to the dynamics of noise transmission, it is possible to choose the most effective solutions for soundproofing purposes. Adopting appropriate solutions does not only mean achieving acoustic insulation results that comply with the DPCM 5/12/1997 on the passive acoustic requirements of buildings, but it can mean “obtaining results appropriate to the desired living comfort” by the tenants of the house. According to the principles of transmission of sound energy, noise has two different components, one direct and the other indirect. In the case of a noise caused by impact, a vibration is propagated VIA SOLID (direct component) and to limit the transmission it is necessary to use soft, flexible materials, able to dissipate the vibrating energy (mechanism of “mass / spring / mass”). The noise, on the other hand, which is transmitted in the form of a sound wave VIA AIR (indirect component) can be attenuated through the adoption of safety measures in the construction elements (increase in the mass or thickness of the materials) or through the reduction of the level sound pressure (sound absorption with specific products).
 Standards
Standards
The concept of acoustic requirement was introduced in general form in Italy with the framework law on noise pollution n. 447 of 30 October 1995 which, entrusting the implementation of the requirements to subsequent decrees, laws and measures, first identifies the figure of the technician competent in acoustics, then the methods of certification of the acoustic characteristics of the products and of the design of buildings, and finally indicates how to carry out the classification of the territory for acoustic purposes and the control and authorization methods for building.
The Decree implementing law no. 447 on noise pollution is issued by the President of the Council of Ministers on December 5, 1997 establishing the passive acoustic requirements of buildings and at the same time classifying the categories of intended use according to TABLE A as published in the Prime Minister’s Decree of 12/05/1997.
The DPCM 5/12/1997 through TABLE B establishes the acoustic insulation that partition walls and facades must guarantee, the level of impact noise of the floors and the maximum noise allowed for the systems operating inside the building, divided into in turn based on continuous operation (boilers, air conditioners, etc.) or discontinuous (lifts, plumbing systems and drains). The limits of the decree are imposed on site, therefore it is essential to take into consideration the real performance of the products used, the effects deriving from their insertion in the particular building context and above all the accuracy of the installation which can be decisive for the final result.

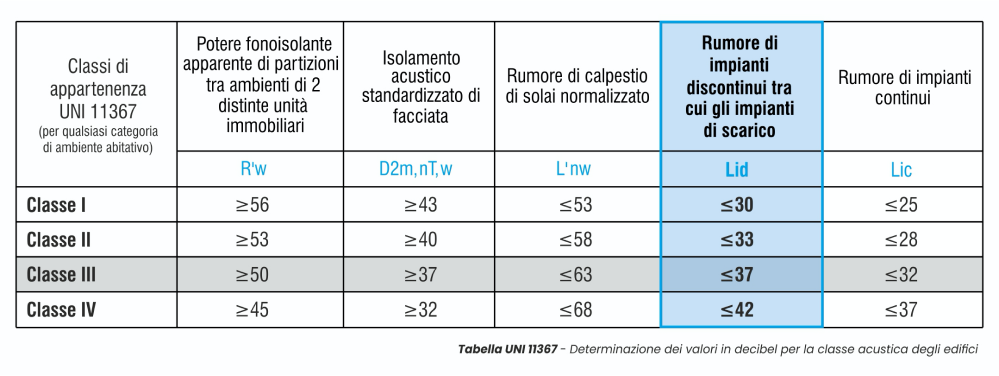
An important step towards the acoustic quality of buildings as a further criterion for evaluating the real estate market was made with the publication, on July 22, 2010, of the Technical Standard UNI 11367 for acoustic classification. Basically, at the end of the construction work, the technician responsible for acoustics performs a wide series of on-site measurements certifying the class to which each of the 5 control descriptors of the acoustic requirement belongs, regardless of the intended use of the building. The weighted average of the values referring to the five descriptors found on site will establish the definitive class of the housing unit which, in the case of UNI 11367, is divided into 4 classes of belonging.
With the application of UNI 11367 the concept according to which: “To achieve the best results it is essential to carefully control all the phases that converge in the construction process: the design, execution of the works, installation materials, construction management, any checks during construction “. In this way the acoustic class becomes a tangible element of objective certification and economic evaluation of the property for the protection of the buyer, as well as for the benefit of construction companies, designers and manufacturing companies that invest in quality. It should be emphasized that the application of the UNI 11367 technical standard on the acoustic classification of buildings remains an optional and not mandatory action. Therefore, in many cases, where not proposed by the builder, it must be requested by the client or by the buyers of the property. As you can see, in the UNI 11367 TABLE in which the values for determining the acoustic class are represented, CLASS III is considered as a class with “basic quality” because it can be approached to the values established by the DPCM 5/12/1997 currently in force and by comply by law in Italy..
Compliance with the acoustic requirement of a building is established by law by Prime Ministerial Decree 5/12/1997 and the suitability of the property is closely linked to it. Failure to comply with this requirement implies a defect in the property that affects its value or its use.
Art. 1490 of the civil code establishes that the seller is required to ensure that the thing sold is free from defects that make it unsuitable for the use for which it is intended or appreciably decrease its value. In the presence of defects, the buyer can request the termination of the contract at his choice (ie the dissolution of the contract with the return of the amount paid) or the reduction of the price. The buyer loses the right to the guarantee if he does not report the defects to the seller within 8 days of discovery, except for a different term established by the parties. The report, however, is not necessary if the seller has acknowledged the existence of the defect or has concealed it. The action is prescribed, in any case, within 1 year from the delivery of the purchased good (Art. 1495 of the Civil Code).
The acoustic defect is one of the serious defects of the property as it significantly affects the enjoyment and use of the home. Consequently, it affects the proper function of the property (Cassation January 27, 2012 n. 1190). This situation is governed by Article 1669 of the Italian Civil Code. The rule provides that if the property has “serious defects, the contractor is liable to the client and his successors in title, provided that the complaint is made within 1 year of discovery”. In this regard, see the sentence of the Court of Milan of 13 November 2015, no. 12818; a ruling which reaffirmed that defects due to inadequate sound insulation are attributable to serious construction defects referred to in art. 1669. In the case of Art. 1669 cc the guarantee on the real estate property extends to 10 years from the delivery of the property. The article can also be invoked against the builder-seller, the designer and the construction manager.
The compliance of a plumbing and heating system is subject to compliance with the law in force regarding compliance with the acoustic requirement according to DPCM 5/12/1997. The declaration of conformity of a plumbing system must be drawn up in compliance with the Decree of the Ministry of Economic Development 22 January 2008, n. 37 – Regulation concerning the implementation of article 11-quaterdecies, paragraph 13, letter A of law no. 248 of 2005, reorganizing the provisions regarding the installation of systems inside buildings (published in the Official Gazette no. 61 on 12 March 2008). The decree applies to systems placed at the service of buildings, regardless of their intended use, located inside them or related appurtenances. At the end of the works, after carrying out the checks required by current legislation, including the functionality of the plumbing system, the installing company issues the customer with the declaration of conformity of the systems built in compliance with the rules referred to in Article 6 of the Ministerial Decree 37 of 22/01/2008. The report containing the type of materials used, as well as the project referred to in Article 5 of the Ministerial Decree 37 of 22/01/2008 must be an integral part of this declaration.
 Rules
Rules
Taking into account that among the elements of a plumbing and heating system that most cause annoying acoustic disturbances are the drainage pipes, the sanitary appliances, the toilet flush cisterns, the siphons, it becomes essential to know the rules for a correct design and installation of the discharge system.
A drainage system can be defined as the system composed of pipes, fittings and other components intended for the drainage of waste water by gravity deriving from sanitary services (bathrooms, kitchens, laundries, etc.) and from industrial and laboratory equipment. To ensure effective evacuation of wastewater, without unpleasant acoustic effects, ebbs and diffusion of foul-smelling fumes in the rooms, it is very important to take care of the design and construction of the discharge system by evaluating some fundamental factors:
- the quantity discharged,
- the simultaneous use of sanitary appliances,
- the maximum flow rate of the pipes,
- the flow speed,
- the necessary air flow to the ducts to avoid pressure and depression phenomena.
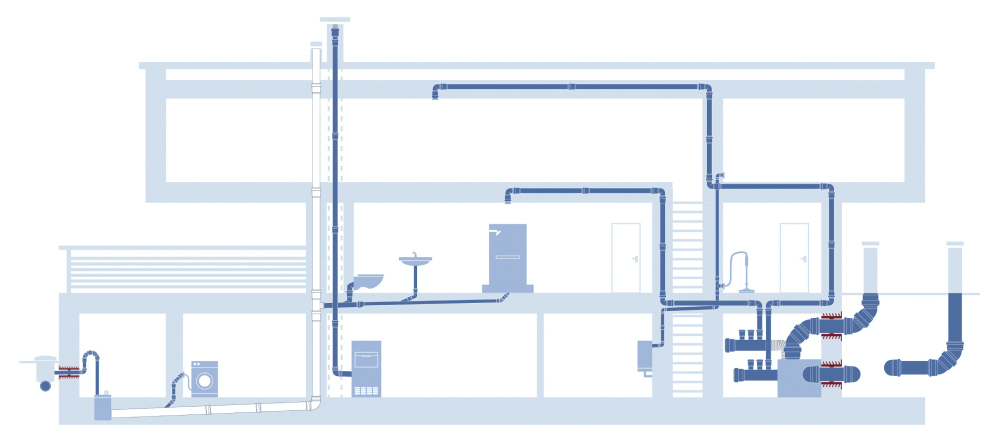
All the technical indications disclosed by Bampi through the PLANNING AND LAYING MANUALS of the drainage systems, are inspired by the UNI EN 12056: 2001 standard and are intended as an orientation guide for a rough designing of the system in Italy and in most of the Community European.
Taking into account the compliance with the UNI EN 12056: 2001 standard for the correct design of the exhaust system, performance results must be achieved that ensure adequate living comfort inside the home. Sizing, designing and installing the drainage system with care and in a workmanlike manner means ensuring its proper functioning, which is not trivial, favoring the conditions to avoid a whole series of problems well known to tenants, such as:
- noises of flowing effluent;
- gurgling effects caused by the emptying of the siphons;
- foul-smelling fumes;
- effects of slowing down the flow in the drains;
- toilet flushing noises;
- pressure effects in sanitary facilities.
A timely and scrupulous design must necessarily be followed by a careful choice of materials within a “plant system”. The subsequent “construction management” process must guarantee control over the correct installation of the systems. Despite forecast reports, especially in the acoustic field, it is essential that the “delicate knots” of the drainage system are treated with the utmost attention during the installation phase to avoid annoying and irreparable discrepancies.
![]() Solutions
Solutions
To avoid the hydraulic and acoustic problems that can negatively characterize the functioning of the drainage system, it is necessary to know its components, the design rules and the precautions to be followed scrupulously in the installation phase. Only by knowing the behavior and operating characteristics of the various components of the drainage system, it will be possible to choose the most suitable and acoustically performing solutions.
The drainage system collects wastewater from users through the sanitary appliances and, with the horizontal branches generally passing through the floors, evacuates them first towards the vertical column and then towards the sewer connection for final disposal through the horizontal collector placed at the base of the building. Since the outflow occurs by simple gravity, it is essential to position the horizontal pipes with the due slopes and to ensure the necessary ventilation of the system to avoid depression and leave the water level inside the siphons unchanged.
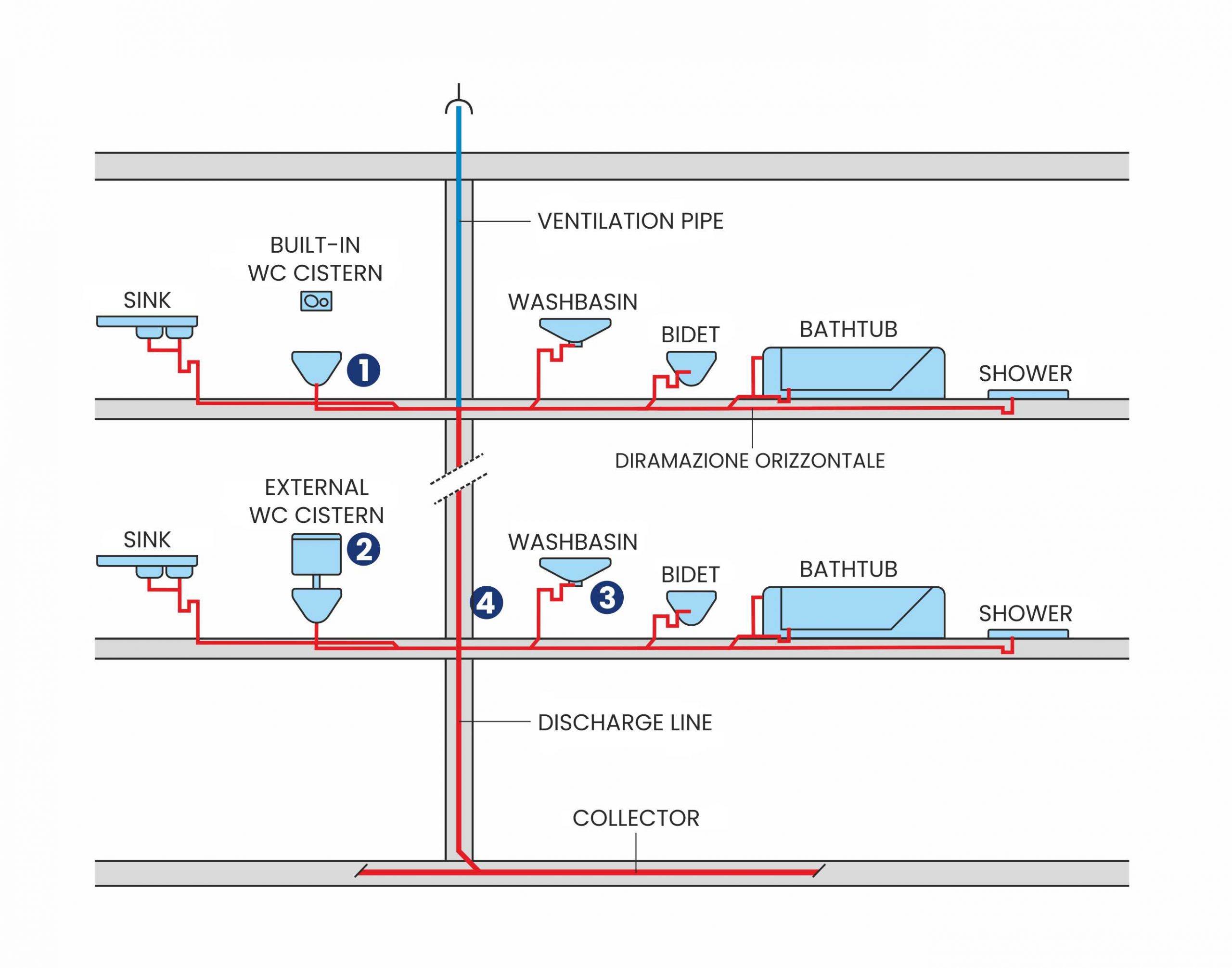
The fundamental attention in terms of sound insulation must focus on some components of the waste system: the toilet bowl, the toilet cistern, the siphons of the sanitary appliances and the vertical column. These elements can be particularly annoying sources of noise on which it is necessary to intervene in the phases of choice of materials and installation:
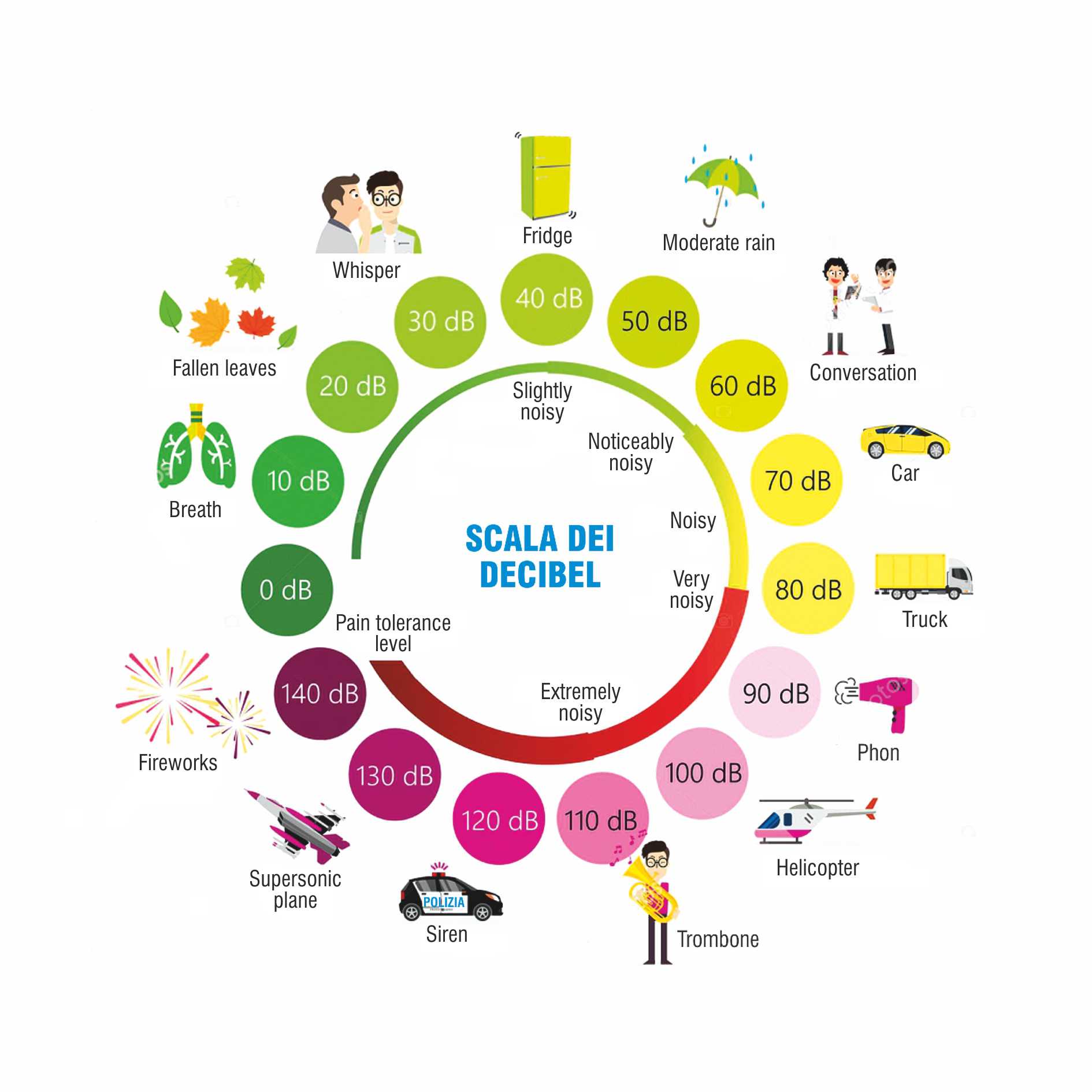
By operating the cistern, 9 to 3 liters of water enter the toilet (depending on the manufacturer’s flow rate calibration of the toilet cistern) in a time ranging from 3 to 5 seconds: this operation, necessary for cleaning, determines a particularly intense and annoying airborne noise, although short, that the toilet bowl tends to amplify inside the service room as a sort of megaphone, while the direct transmission of vibrations spreads rapidly by contact through the ceramic floor covering and walls.
Bampi solutions to avoid toilet flushing noise are:
• FONOdBAM Isolating sheath for drainage systems
• FONECOdBAM Soundproofing sheet for exhaust systems
Once its water content has been expelled, the rinsing cistern takes about one minute to refill: this phase is manifested initially with the turbulent noise of water falling into the bottom of the cistern and then with a hiss of constant intensity that lasts until the filling is complete.
Bampi solutions to avoid toilet filling noise are:
• BSILENT Soundproof concealed toilet flush cistern
• VELA External soundproof toilet flush cistern
• MAGNETIC Universal soundproof fill valve
• MAGIK Universal soundproof fill valve
During the use of sanitary appliances, and especially when rinsing the toilet, the air sucked in by the siphons closest to the slab (shower, bathtub or bidet) causes a sort of gurgling which, in the worst cases, is immediately followed from a return of foul-smelling fumes inside the room. The acoustic effect of the “gurgling” is often perceived even when the unloading phase of household appliances (washing machine or dishwasher) connected directly to a sink is in operation.
Bampi solutions to avoid depression noise are:
• BAMVENT-110 Air admission valve for drain column
• BAMVENT-50 Air admission valve for sanitary users

The wastewater coming from the horizontal branches, once it reaches the vertical discharge column, begins to descend, gaining speed and the flow manifests itself towards the rooms hosting the system in the form of a shower and then of dripping.
Bampi solutions to avoid flushing noise are:
• POLO-KAL 3S High performance soundproof drainage system
• POLO-KAL XS Latest generation soundproof drainage system
• POLO-KAL NG Multifunction soundproof drainage system
• ULTRA-SILENT Soundproof and reinforced drainage system
• POLO-CLIP HS Soundproof collar for anchoring the drain columns

 Problems
Problems Standards
Standards Rules
Rules Solutions
Solutions